See History at AAX for a more general timeline.
600 BCE
- Abacus - Commonly credited to the Chinese but may have originated in the Middle east.
The oldest surviving abacus was used in 300 B.C. by the Babylonians.
May have evolved from counting tables on a simple stone slab with incised parallel lines around 3000 BCE.
1925 - Vannevar Bush at MIT develops analog computers, culminating in the
Differential Analyzer in the early 1940's
1945 - Bush authored the article "As We May Think" in the Atlantic Monthly
in which he first proposed his idea of the Memex machine, which would help people
sort through the enormous amount of published information available throughout the world.
1947
- Bell Labs (Walter Brattain and William Shockley) invents the transistor.
1958
- The integrated circuit (IC) is invented by Jack St. Clair Kilby of Texas Instruments,
beating Robert Noyce of Fairchild Semiconductor who independently invented one in 1959.
Noyce went on to cofound Intel.
- FLOW-MATIC, originally known as B-0 , was the first English-like data processing language.
It was developed for the UNIVAC I at Remington Rand under Grace Hopper.
It was the first machine-independent programming language,
and led to the development of COBOL.
1963
- Douglas Engelbart patents the mouse while at Stanford Research Institute (SRI).
- Ivan Sutherland develops Sketchpad using a light pen and bitmap display to make
CAD like drawings on a computer screen as part of his PhD thesis at MIT.
- It takes 20 years for these two technologies to be combined into a personal
computer (Apple Lisa, Xerox Star and Macintosh)
1964
- John George Kemeny and Thomas Eugene Kurtz develop the BASIC
(Beginner's All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) language at Dartmouth.
1965
- Digital Equipment produced the first PDP-8 minicomputer,
the first production computer to use integrated circuits.
- Time sharing systems by companies like GE's GEISCO and Tymshare,
using terminals connected to computers like the SDS 940, the PDP-10, and the IBM 360
with Bell 103 (110 baud) modems to access things like BASIC programming.
- Gordon E. Moore (Intel co-founder) describes "Moore's law": The number of transistors
that can be placed on an IC will double approximately every two years.
1968-9
- Bell Labs scientists start work on the C programming language and new OS
for the DEC PDP-7 with 8K 18-bit words of memory .
1970
- Ken Thompson and Dennis Ritchie at Bell Labs develop UNIX operating system (OS).
A portable, multi-tasking and multi-user in a time-sharing system running on a DEC PDP-7
1972
- INTEL released the 200 kHz 8008, an 8 bit version of the 4004
- Clive Sinclair is the first (August 1972) to bring a pocket calculator
TI and HP follow shortly
- Arcade video game Pong developed
- Xerox starts project "Alto", to build a personal computer at
the Palo Alto Research Center (PARC).
The mouse and bitmap displays had been invented 10 or more years earlier
but researchers such as Alan Kay, Larry Tesler, Dan Ingalls and others developed
the Graphical User Interface (GUI)
using the mouse to point-and-click and drag-and-drop icons
(small intuitive pictograms representing a function or data).
What You See Is What You Get (WYSIWYG) text editing was also part of their system.
They develop the icon based graphical user interface later popularized by
the Apple Macintosh (1984) and Microsoft Windows 3 (1990)
- Bell Labs Programing Language C used internally.
1973
- E-mail standards for exchanging messages over Arpanet are created by Ray Tomlinson of BBN.
Timesharing systems in the early 60's had programs to exchange text messages with users.
- A Canadian firm, Automatic Electronic Systems, introduced the world's first
programmable word processor with a video screen" the AES 90.
Wang, VYDEC, and Lexitron follow shortly
- Steve Wozniak builds a "blue box" tone generator to make free phone calls
and sells them in the dorm at UC Berkeley.
- At Xerox PARC, Alan Kay proposes they build a portable personal computer: the Dynabook
- The UNIX OS is rewritten in C (It was previously in assembly language)
1974
- The CP/M (Control Program/Monitor also: Control Program for Microcomputers)
designed by Digital Research /John Torode and Gary Kildall for the 8080 chip.
- The Z-80, 8 bit processor is designed by Zilog Corp.
- Intel introduced the 8080 for the purposes of controlling traffic lights,
but it was to find fame later as the processor for the Altair.
- Motorola introduces the 6800 CPU, an early 8 bits microprocessor
that will be embedded in a lot of industrial devices.
- First Use of term "Internet" appears in a conference paper by Vinton Cerf and Bob Kahn.
1975
- Ed Roberts (USA) starts to ship the MITS ALTAIR 8800, with the Intel 8080 chip
It contains a memory of 256 bytes, a row switches in stead of a keyboard
and led that serves as a read out in stead of a monitor.
- Micro-Soft is founded by Bill Gates and Paul Allen.
Their first product is a version of BASIC for the ALTAIR.
1976
- The 6501 and 6502 micro processor was developed by MOS Technology Corporation.
1977
- Dennis C. Hayes invents the PC modem
- Apple (Steve Wozniak and Steve Jobs) introduces the Apple II for $1,300
- Interactive System Corp. starts selling Unix commercially.
- Commodore developed the PET 2001 based on the 6502 chip
- Bill Joy at UC Berkeley starts distributing a variation of Bell Labs UNIX called
Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). Originally an add-on to Bell Labs UNIX.
1978
- INTEL introduced the 16-bit-8086 chip and the coprocessor 8087.
- The first 64 Kb (8 KB) RAM memory chip were being produced in mass by IBM.
- Personal Software (Dan Bricklin and Bob Frankston) released VisiCalc for the Apple II
- The first BBS (Bulletin Board System) created by Ward Christen
- Texas Instruments introduced a computer for kids, the Speak & Spell talking learning aid
- Atari announced the Atari 400 and 800 personal computers both with a 6502 CPU
1979
- Oracle introduces the first commercial SQL relational database management system.
- WordStar word processor for PCs
- Space Invaders and Pacman games introduced
- Xerox (Bob Metcalfe), DEC and Intel introduced the "Ethernet" standard for local networks.
- CompuServe and The Source on-line services open.
- Apple had a business arrangement with Xerox which allowed Steve Jobs to visit PARC;
Whether they actually licensed the GUI is unclear.
See: Did Apple license Xerox PARC's GUI at quora.com
- Apple starts development on the Macintosh and in 1980 hires Larry Tesler from Xerox PARC.
1980
- Seagate Technology introduces the first hard disk drive for microcomputers, the ST506.
5 Mb. The access time is low: 180 - 240 milliseconds
- HP, Xerox and others come out with CP/M based PCs. CP/M ported to Apple II.
1981
- First IBM PC - 4.77 MHz 8 bit 8088 CPU of Intel 64KB RAM, 40KB ROM,
one 5.25-inch floppy drive (160KB capacity) for $1,565.
There are various stories about why IBM used DOS (Disk Operation System) instead of CP/M
The most common is IBM approached Digital Research (DR) to use their CP/M operating system.
Gary was not available and Mrs. Kildall refused to sign the contract/non-disclosure.
See: Switch from CP/M to DOS by Bill Gates.
History of MS-DOS at DigitalResearch.biz
- Microsoft bought all rights to an OS from Seattle Computer Products then called QDOS
assumingly meaning Quick and Dirty Operating System, and the name PC-DOS is adopted.
Story is that part of QDOS was copied from CP/M and DR eventually won a settlement.
- The original DOS architecture had a 640 KB memory limit.
Bill Gates says "640K ought to be enough for anybody."
- Osborne 1 is the first "portable" computer
1982
- ARPA enacts TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and Internet Protocol (IP)
and the DOD adopts it as its standard.
- Xerox introduces the STAR based on ALTO for $16,000
The first WIMP environment (Window, Icons, Mouse and Pull-down menus) PC.
- Time Magazine eschewed its Man of the Year Award in favor of Machine of the Year:
- Ashton Tate releases the database program dBase II.
- Sun Microcomputer corporation is founded, by Scott McNealy, Bill Joy and others.
The SunOS operating system based on the Unix dialect 4.2 BSD
1983
- CSNet linked with TCP/IP Gateways to ARPANet forming the Internet.
- IBM PC sales have exceeded IBM estimates thru 1989
- Apple introduces LISA for $4,500.
- CSNet linked with TCP/IP Gateways to ARPANet forming the Internet.
- Mitch Kapor develops Lotus 1-2-3 spread sheet which becomes the top selling software
for many years.
It added integrated charting, plotting and database capabilities to the Visicalc model.
- Radio Shack TRS-80 Model 100 - One of the first laptop computers for $1,099.
- Microsoft introduces the Micorsoft Mouse to use with Microsoft Word
with the DOS operating system. It cost $200 and required a special card
plugged into the system bus in your PC.
1984
- Apple introduces Macintosh for $995 with the Orwellian commercial, during the Superbowl.
Team included Steve Jobs, Bill Atkinson, Andy Hertzfeld, Guy Kawasaki and many others.
See: The Wizards behind the Macintosh and 25 years of Mac at Mac-History.net
- MS-DOS 3.0
- C++ (C with classes) programming language released by Bell Labs
1985
- Microsoft announces Windows Operating System 1, but it is not very successful.
- Novell introduces Advanced NetWare 2.0
- Microsoft Excel released for the Macintosh
- Commodore releases Amiga with a multi-tasking operating system and a 4096 color display.
It had a significant technical lead on its three main competitors
(the Atari ST, the Macintosh and the IBM PC)
1986
- IBM and Microsoft release OS/2 a multitasking OS with a text interface.
- Eric Graham shows his "Juggler" demo animation on the Amiga, showing the
Amiga's capabilities of ray-traced animation merged with digitized sound.
1987
- Microsoft releases Excel for DOS
1988
- Microsoft surpasses rival Lotus Development Corporation as the top software vendor.
- Robert Morris launches the infamous "internet worm",
ushering in the age of widespread worms, viruses and trojan horses.
- ISDN service trials to provide 128 kbit/s Internet access over phone lines
1989
- Tim Berners Lee invents software for the World Wide Web while working at CERN,
a high-energy physics lab in Switzerland.
1990
- Windows 3.0 released, the first really (semi) usable version of Windows.
- Excel 3.0 released
1991
- Linus Torvalds starts working on Linux based on GNU and MINUX, with many of
the features of UNIX.
- Apple releases Mac System 7 a major upgrade.
System 7 allowed users to access PC networks and allowed communication via TCP/IP
It paved the way for a full 32-bit address space.
1992
- Windows NT (New Technology) 3.1 released. (called 3.1 for consistency with Windows)
A basic redesign to support high-end, client/server business applications.
It no longer ran on top of DOS (Disk Operating System)
- Novell purchases UNIX from AT&T
1993
- Marc Andreessen working for NCSA at UIUC creates the Graphical Web Browsers Mosaic
- Apple Newton personal digital assistant (pda) with handwriting recognition,
which doesn't work very well.
- Apple releases the color classic, their first computer with a color display.
1994
- Jim Clark starts Netscape Inc. and brings Mark Andresen on.
- Yahoo Web search service founded.
- V.34 (28.8kbs) modem standard
1995
- Novell sells UNIX to SCO
- Microsoft introduces Windows 95 (almost as good at the Mac System 7 [1991])
First version with 32-bit runtimes.
Support for long file names of up to 255 characters.
See Macintosh vs. Windows 95 at Mac Musings
1996
- Jeff Hawkins, Donna Dubinsky, and Ed Colligan invent the palm pilot
A PDA (personal digital assistant) with notes, a calendar, todo list, address book
and a touch sensitive screen which recognizes a stylized "gratfiti" handwriting via a stylus.
1997
- Cable modems allow Internet access at speeds up to 10 Mbs over cable TV services.
1998
- Google search engine started
- RIM introduces its first BlackBerry, a wireless handheld computer and phone.
- Linux becomes mainstream with commercial implementations.
- V.90 (56kbs) modem standard issued
- DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) services to provide simultaneous voice and data
(256 Kbs - 1.5 Mbs)
- United States v. Microsoft was a set of consolidated civil actions filed
against Microsoft Corporation pursuant to the Sherman Antitrust Act.
The central issue was whether Microsoft could bundle its Internet Explorer (IE)
web browser software with its Windows OS. The court ruled
that Microsoft must be broken into two separate units, one to produce the
operating system and another for applications. It was overturned in 2000.
1999
- Wi-Fi 802.11b wireless networking (up to 11 Mbs) devices begin shipping.
2001
- Microsoft releases windows XP, the first consumer-oriented operating system
built on the Windows NT kernel. It came in 32 bit and 64 bit versions.
2002
- Handspring introduces Treo (combined phone and pda). Palm later buys Handspring.
2003
- Wi-Fi 802.11g wireless networking (up to 54 Mbs) devices begin shipping.
- Mac OS X 10.4 "Tiger" provides limited support for 64-bit
applications on machines with PowerPC 970 (G5) processors
2006
- Sony reader with E Ink for reading ebooks. 35 years after Alan Kay proposes dynabook.
- Apple switches form PowerPC processors to Intel processors.
Boot Camp allows Intel-based Macs to run Windows XP
2007
- Apple releases the iPhone
- Amazon releases the Kindle e-reader
- Verizon offers fiber to the home, FIOS
2008
- 3G (third generation) (500 Kbs - 1.5 Mbs) mobil phone networks implemented
2009
- Smartphones take off. There is no definition of a smartphone, but they
generally have computer and pda features like email access and small keyboards.
- 802.11n Wi-Fi components available for speeds over 100 Mbps.
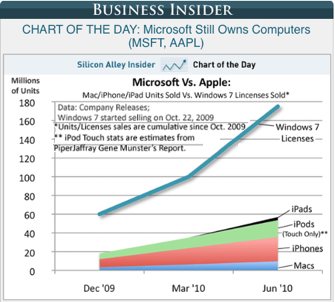 2010
- iPad - Apple tablet - Fifth screen (1. Movies, 2. TV, 3. Computer, 4. Mobile (phone), 5. iPad)
2010
- iPad - Apple tablet - Fifth screen (1. Movies, 2. TV, 3. Computer, 4. Mobile (phone), 5. iPad)
Although Apple's net worth and market share exceeds that of Microsoft, Microsoft still leads in volume and market share.
2011
Steve Jobs (Apple) and Dennis Ritchie (UNIX) pass away. See Simple and beautiful.
Terms:
Prefixes: (see Internet-related prefixes - Wikipedia)
- The term 'cybernetics', from the Greek adjective κυβερνητικός meaning skilled in steering or governing, was coined in Norbert Wiener's book Cybernetics or Control and Communication in the Animal and the Machine (MIT Press, 1948).
In the 1970s, the Control Data Corporation (CDC) sold the "Cyber" range of supercomputers.
In 1983 William Gibson coined the term as "cyberspace" in his cyberpunk science fiction novels.
- E-, standing for electronic, started with e-mail around 1971. E-business, E-commerce, e-banking and e-books. were widely used in the 1990's. e-readers (Sony Reader, kindle, nook) were introduced in 2006-7.
- i-, Attributed to Apple with the iMac in 1998, and used for iPod, iTunes, iLife, iPad, ... "i" stands for Internet.
Links:
Steve Jobs and Bill Gates interviews at the D5 Conference (All Things Digital) - 2007
Word Processing History
Timelines:
Timeline of Microcomputers at FortuneCity.com [1926-1970][1971-1976][1977-1980][1981-1983][1984-1986][1987-1990][1991-1993][1994-1996][1997-1999][2000-2001]
[2002-]
Timeline of Microcomputers (1981-1983)
History at AAXnet
Internet History and Internet/Hypertext Timeline
The history of computing project
Computer History Museum
Apple history at the Steve Jobs page.
Return to Computing
last updated 2 Feb 2010
|
 Computing
Computing
 Mini and Personal Computing Timeline
Contact
Mini and Personal Computing Timeline
Contact
 Computing
Computing
 Mini and Personal Computing Timeline
Contact
Mini and Personal Computing Timeline
Contact
 2010
- iPad - Apple tablet - Fifth screen (1. Movies, 2. TV, 3. Computer, 4. Mobile (phone), 5. iPad)
2010
- iPad - Apple tablet - Fifth screen (1. Movies, 2. TV, 3. Computer, 4. Mobile (phone), 5. iPad)